
Using a pacemaker to regulate heartbeats, or implanting an automatic implantable cardioverter defibrillator (AICD) may also be taken into considerations.

To treat heart arrhythmia, the doctor may consider prescribing oral medications to control the condition, and in that case the patients will have to take the pills for the rest of their lives. The doctor will assess and choose the proper diagnostic test for each patient. Diagnosis and treatment of Heart A rrhythmiaĭoctors initiate the diagnosis of heart arrhythmia by taking medical history from the patient, perform physical examinations, record electrical signals from the heart using electrocardiogram (EKG) or a 24 hour Holter monitor or conducting an electrophysiological study. And if symptoms occur, treatment can be received right away. Thus, if suspicious symptoms of heart arrhythmia arise such as palpitations, fast heartbeats, dizziness or fainting, see a doctor immediately for further investigations. However, those who have never had symptoms of heart arrhythmia may also experience irregular heartbeat. For instance, diabetes, high blood pressure, stress and taking or receiving certain drugs or chemical substances such as amphetamine and caffeine.
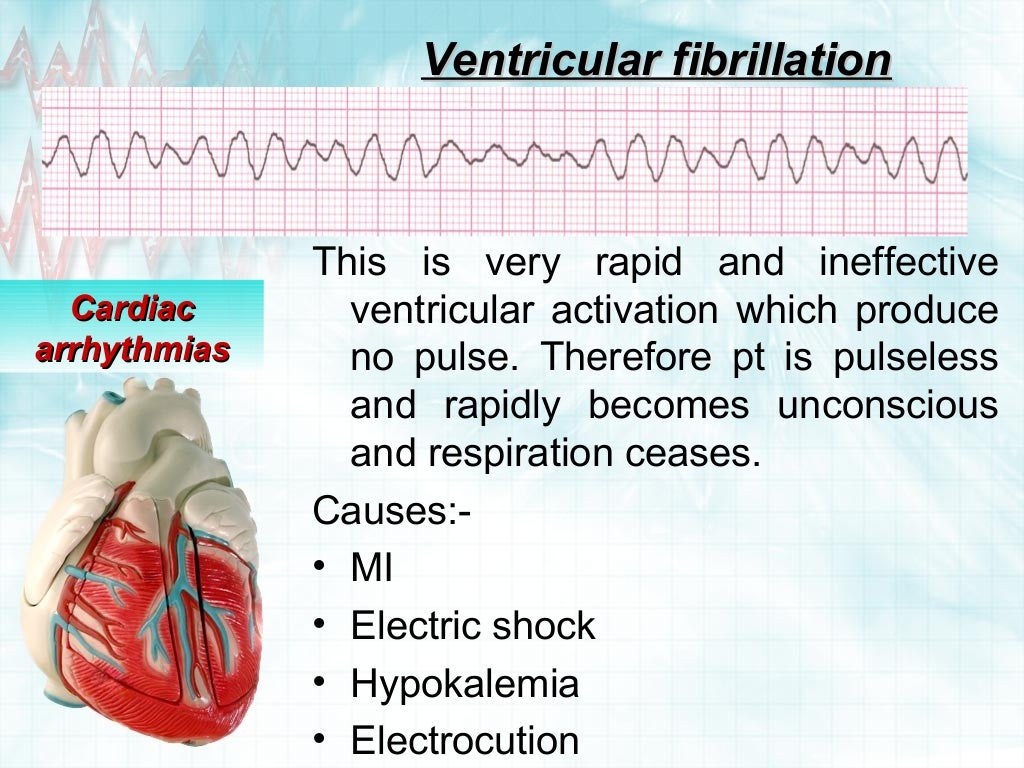
For example, congenital heart disease, cardiomyopathy and leaky heart valves, as well as other disorders that have impacts on the heart function. It could be due to changes to the heart structure. Heart arrhythmia could be caused by many reasons. People who are at risk of developing Heart Arrhythmia The treatment comprise the use of medications to control the heart rate, regulating the heartbeat with a pacemaker, implanting an automatic implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (AICD), as well as performing ablation with a radiofrequency catheter. There are many ways to treat heart arrhythmia, depending on the abnormality of the symptoms and the severity. More importantly, detecting the disease from an early stage will make the treatment process less complicated. Seeing a specialist early will allow the doctor to diagnose and make a treatment plan in the right time. Heart arrhythmia is classified into two types: fast heartbeat and slow heartbeat. By the time they become aware of it, the symptoms progressed or other complications developed. Have you ever experienced tiredness, palpitation, fainting, or falling unconscious? They might be signs of heart arrhythmia which often time patients don’t rush to see a doctor even after having the symptoms. Pinpointing the cause of your arrhythmia helps us take a proactive approach to treatment, prevents the possibility of sudden cardiac death, and ensures your family is well-informed of any increased risk.Tiredness, heart palpitations are the signs of Heart Arrhythmia Our genetic heart disease program is one of the only programs in the Southeast with experts who can administer and interpret the complex tests required to identify inherited heart rhythm disorders such as long QT and Brugada syndromes. Specialized Procedures for Less-Common Arrhythmiaĭuke is among a handful of centers with substantial expertise in epicardial catheter ablation, which treats ventricular tachycardia that occurs on the heart’s outer surface. Over the past two years, fewer than 10% of our patients have needed a repeat ablation - a rate less than half the average. As a result, the problem area is treated and the likelihood of repeat procedures is reduced.

Computer-guided treatments stabilize the catheter and more accurately guide its movement within the heart. Your cardiac ablation will be performed by electrophysiologists trained in the most advanced ablation techniques available, including heart mapping for spiral waves and focus beats, which can shorten procedure time. Our research and expertise help set the standard for arrhythmia treatment nationwide. We continually evaluate new treatment approaches and have achieved some of the lowest complication rates associated with cardiac ablation, a common treatment for atrial fibrillation ( Afib) and ventricular tachycardia. Our specially trained electrophysiologists treat nearly 1,700 people with arrhythmias each year - among the highest number in the Southeast. Setting the Standard for Arrhythmia Treatment


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
